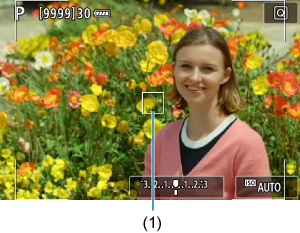
Selecting the AF Method (Live View Shooting)
- AF Method
- Selecting the AF Method
(Face)+Tracking:
- Spot AF / 1-Point AF / AF Point Expansion (
) / AF Point Expansion: Around / Zone AF / Large Zone AF: Vertical / Large Zone AF: Horizontal
- Magnified View
- AF Shooting Tips
- Shooting Conditions That Make Focusing Difficult
- AF Range
AF Method
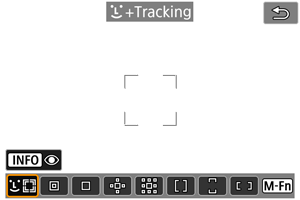
 : Face+Tracking
: Face+Tracking
The camera detects and focuses on people's faces. An AF point appears over any face detected, which is then tracked.
When no face is detected, focusing areas are determined not only based on the nearest subject but also based on a variety of other conditions such as subject motion and distance.
With Servo AF, you can set the initial position for Servo AF (). As long as the Area AF frame can track the subject during shooting, focusing will continue.
 : Spot AF
: Spot AF
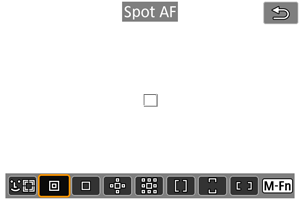
The camera focuses in a narrower area than 1-point AF.
Effective for pinpoint focusing or focusing on overlapping subjects such as an animal in a cage.
Note that the small Spot AF area may make focusing difficult in handheld shooting or for moving subjects.
 : 1-point AF
: 1-point AF
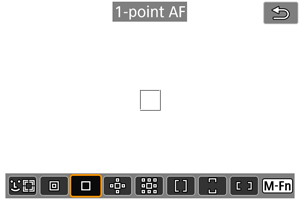
The camera focuses using a single AF point .
 : Expand AF area:
: Expand AF area: 
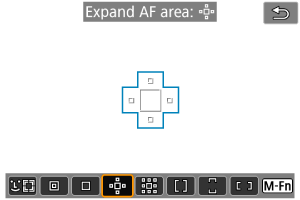
Focuses using one AF point and AF points outlined here in blue. Effective for moving subjects, which are difficult to track with 1-point AF.
Focusing on your preferred subject is easier than with Zone AF.
When Servo AF is used, first you will focus using an AF point .
 : Expand AF area: Around
: Expand AF area: Around
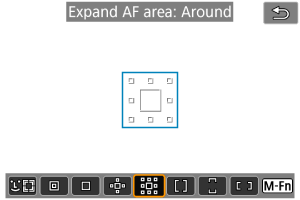
Focuses using one AF point and surrounding AF points outlined here in blue, which makes it easier to focus on moving subjects than with AF point expansion (
). Servo AF operation is the same as for AF point expansion (
).
 : Zone AF
: Zone AF
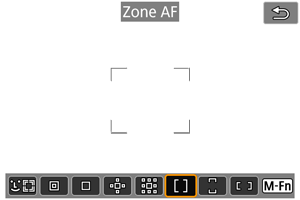
Uses auto selection AF in Zone AF frames to cover a larger area than AF point expansion, which makes focusing easier than with AF point expansion.
Focusing areas are determined not only based on the nearest subject but also based on a variety of other conditions such as faces, subject motion, or subject distance.
AF points in focus are displayed with .
 : Large Zone AF: Vertical
: Large Zone AF: Vertical
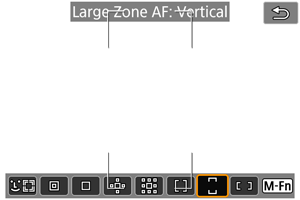
Uses auto selection AF in a vertical Large Zone AF frame to cover a larger area than Zone AF, which makes focusing easier than with 1-point AF/AF point expansion and also effective for moving subjects.
Focusing areas are determined not only based on the nearest subject but also based on a variety of other conditions such as faces, subject motion, or subject distance.
AF points in focus are displayed with .
 : Large Zone AF: Horizontal
: Large Zone AF: Horizontal
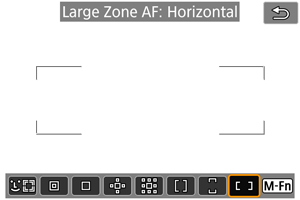
Uses auto selection AF in a horizontal Large Zone AF frame to cover a larger area than Zone AF, which makes focusing easier than with 1-point AF/AF point expansion and also effective for moving subjects.
Focusing areas are determined not only based on the nearest subject but also based on a variety of other conditions such as faces, subject motion, or subject distance.
AF points in focus are displayed with .
Selecting the AF Method
-
Press the
button.
-
Select the AF method.
- Each time you press the
button, the AF method changes.
- Each time you press the
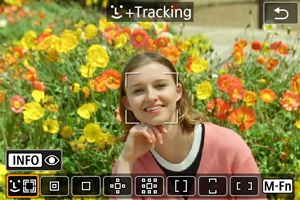
 (Face)+Tracking:
(Face)+Tracking: 
The camera detects and focuses on people's faces. If a face moves, the AF point also moves to track the face.
You can set [: Eye Detection AF] to [Enable] to shoot with the subject's eyes in focus ().
-
Check the AF point.

- An AF point
appears over any face detected.
- To choose a face to focus on when multiple faces can be detected, press the
button to change the AF point to
, then use
. As you use
, the AF point changes again to
.
- You can also tap the screen to choose a face.
- An AF point
-
Focus and take the picture.

-
Once you press the shutter button halfway and the subject is in focus, the AF point turns green and the camera beeps.
An orange Area AF frame indicates that the camera could not focus on subjects.
-
AF point display

After automatic face detection by the camera
(single frame)

After manual face selection
(double frame)
Note
- Selecting a face manually by tapping the screen or using
locks onto that subject for tracking, and the camera tracks the subject even if it moves within the screen. To release locked tracking, tap [
].
Caution
- Tapping the screen to focus will focus with [One-Shot AF], regardless of the AF operation setting.
- If the subject's face is significantly out of focus, face detection will not be possible. Adjust the focus manually () so that the face can be detected, then perform AF.
- An object other than a human face may be detected as a face.
- Face detection will not work if the face is very small or large in the picture, too bright or too dark, or partially hidden.
- AF may not detect subjects or people's faces at the edges of the screen. Recompose the shot to center the subject or bring the subject closer to the center.
- The camera will keep moving the active AF point to track subjects when Servo AF is set, but under some shooting conditions (such as when subjects are small), it may not be possible to track the subject.
Note
- The active
may cover only a part of the face, not the whole face.
- The size of the AF point changes depending on the subject.
Eye Detection AF
With the AF method set to [+Tracking], you can shoot with the subject's eyes in focus.
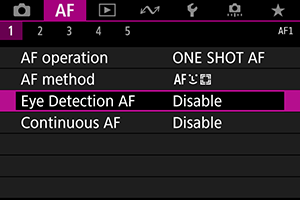
-
Select [
: Eye Detection AF].
-
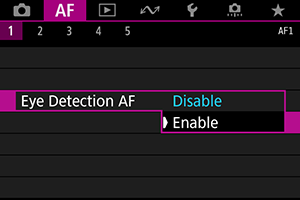
Select [Enable].
-
Aim the camera at the subject.

- An AF point is displayed around their eye.
- To choose an eye to focus on, press the
button to change the AF point to
, then use
. As you use
, the AF point changes again to
.
- You can also tap the screen to choose an eye.
- If your selected eye is not detected, an eye to focus on is selected automatically.
-
Take the picture.
Caution
- Subject eyes may not be detected correctly, depending on the subject and shooting conditions.
Note
- To switch to [Eye Detection AF: Disable] without using menu operations, press the
button and then the
button. To switch to [Eye Detection AF: Enable], press the
button again.
Setting the initial Servo AF position
You can manually set the initial Servo AF position when [: Initial Servo AF pt,
/
] is set to [Initial AF pt set for
/
] ().
Spot AF / 1-Point AF / AF Point Expansion ( ) / AF Point Expansion: Around / Zone AF / Large Zone AF: Vertical / Large Zone AF: Horizontal
) / AF Point Expansion: Around / Zone AF / Large Zone AF: Vertical / Large Zone AF: Horizontal
You can manually set the AF point or Zone AF frame. Here, 1-point AF screens are used as an example.
-
Check the AF point.
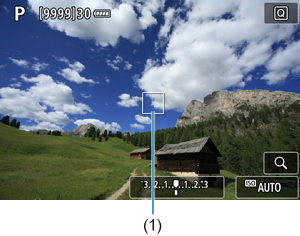
- The AF point (1) will appear.
- With AF point expansion (
) or AF point expansion: Around, adjacent AF points are also displayed.
- With Zone AF, Large Zone AF: Vertical, or Large Zone AF: Horizontal, the specified Zone AF frame is displayed.
-
Move the AF point.

- Use
to move the AF point into position for focusing (but note that with some lenses, it may not move to the edge of the screen).
- You can also focus by tapping a position on the screen.
- To center the AF point or Zone AF frame, press
or the
or
button.
- Use
-
Focus and take the picture.

- Aim the AF point over the subject and press the shutter button halfway.
- When focus is achieved, the AF point will turn green and the beeper will sound.
- If the camera cannot focus, the AF point or Zone AF frame turns orange.
Caution
- The camera continues to switch the active AF point
to track subjects when Zone AF or Large Zone AF (vertical or horizontal) is set to Servo AF, but tracking may not be possible under some shooting conditions, such as when subjects are small.
- Focusing may be difficult when using a peripheral AF point. In this case, select an AF point in the center.
- Tapping the screen to focus will focus with [One-Shot AF], regardless of the AF operation setting.
Magnified View
To check the focus when the AF method is other than [+Tracking], magnify display by approx. 5× or 10× by pressing the
button (or tapping
).
- Magnification is centered on the AF point for [Spot AF], [1-point AF], [Expand AF area:
], and [Expand AF area: Around] and on the Zone AF frame for [Zone AF], [Large Zone AF: Vertical], and [Large Zone AF: Horizontal].
- Autofocusing is performed with magnified display if you press the shutter button halfway when set to [Spot AF], and [1-point AF]. When set to AF methods other than [Spot AF] and [1-point AF], autofocusing is performed after restoring normal display.
- With Servo AF, if you press the shutter button halfway in the magnified view, the camera will return to the normal view for focusing.
Caution
- If focusing is difficult in the magnified view, return to the normal view and perform AF.
- If you perform AF in the normal view and then use the magnified view, accurate focus may not be achieved.
- AF speed differs between the normal view and magnified view.
- Continuous AF and Movie Servo AF are not available when display is magnified.
- With the magnified view, achieving focus becomes more difficult due to camera shake. Using a tripod is recommended.
AF Shooting Tips
- Even when focus is achieved, pressing the shutter button halfway will focus again.
- Image brightness may change during autofocusing.
- Depending on the subject and shooting conditions, it may take longer to focus, or the continuous shooting speed may decrease.
- If the light source changes as you shoot, the screen may flicker, and focusing may be difficult. In this case, restart the camera and resume shooting with AF under the light source you will use.
- If focusing is not possible with AF, focus manually ().
- For subjects at the edge of the screen that are slightly out of focus, try centering the subject (or AF point, or Zone AF frame) to bring them into focus, then recompose the shot before shooting.
- With certain lenses, it may take more time to achieve focus with autofocus, or accurate focusing may not be achieved.
Shooting Conditions That Make Focusing Difficult
- Subject with low-contrast such as the blue sky, solid-color flat surfaces or when highlight or shadow details are clipped.
- Subjects in low light.
- Stripes and other patterns where there is contrast only in the horizontal direction.
- Subjects with repetitive patterns (Example: Skyscraper windows, computer keyboards, etc.).
- Fine lines and subject outlines.
- Under light sources with constantly changing brightness, colors, or patterns.
- Night scenes or points of light.
- The image flickers under fluorescent or LED lighting.
- Extremely small subjects.
- Subjects at the edge of the screen.
- Strongly backlit or reflective subjects (Example: Car with a highly reflective surfaces, etc.).
- Near and distant subjects covered by an AF point (Example: Animal in a cage, etc.).
- Subjects that keep moving within the AF point and will not stay still due to camera shake or subject blur.
- Performing AF when the subject is very far out of focus.
- Soft focus effect is applied with a soft focus lens.
- A special effect filter is used.
- Noise (dots of light, banding, etc.) appears on the screen during AF.
AF Range
The available autofocus range varies depending on the lens used and settings such as recording size and Movie digital IS.