Histogram
The brightness histogram shows the exposure level distribution and overall brightness. The RGB histogram is for checking the color saturation and gradation.
-
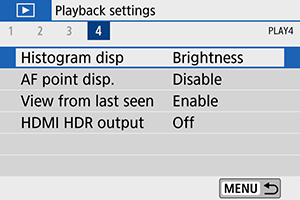
Select [
: Histogram disp].
-
Select an item.
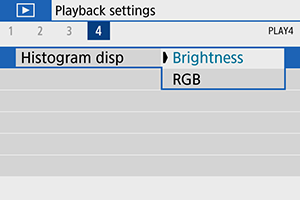
-
[Brightness] display
This histogram is a graph showing the distribution of the image's brightness level. The horizontal axis indicates the brightness level (darker on the left and brighter on the right) while the vertical axis indicates how many pixels exist for each brightness level. The more pixels there are toward the left, the darker the image. The more pixels there are toward the right, the brighter the image. If there are too many pixels on the left, the shadow detail will be lost. If there are too many pixels on the right, the highlight detail will be lost. The gradation in-between will be reproduced. By checking the image and its brightness histogram, you can see the exposure level inclination and the overall gradation.
Sample histograms
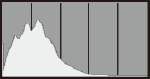
Dark image
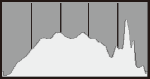
Normal brightness

Bright image
-
[RGB] display
This histogram is a graph showing the distribution of each primary color's brightness level in the image (RGB or red, green, and blue). The horizontal axis indicates the color's brightness level (darker on the left and brighter on the right), while the vertical axis indicates how many pixels exist for each color brightness level. The more pixels there are toward the left, the darker and less prominent the color. The more pixels there are toward the right, the brighter and denser the color. If there are too many pixels on the left, the respective color information will be lacking. If there are too many pixels on the right, the color will be too saturated with no gradation. By checking the image's RGB histogram, you can see the color's saturation and gradation condition, as well as white balance inclination.
