Glossary
- RAW image
- RAW images from EOS camera are recorded in an uncompressed 14-bit or 12-bit format.
- Viewing RAW images requires software with image processing functionality, such as DPP. An advantage of RAW images is that they can be edited with essentially no loss of image quality.
- “RAW” meaning “in a natural condition” or “not processed or refined.”
- JPEG image
- The most common type of image, in an irreversibly compressed 8-bit format.
- Offers the advantage that high compression keeps file sizes small (even for images with a high pixel count), but because saving and compression thins out some data to keep files small, repeated editing or saving gradually reduces image quality.
- With DPP, even repeated editing or saving only modifies the recipe data, without overwriting or compression, which preserves the original image quality.
- JPEG stands for Joint Photographic Experts Group.
- TIFF image
- Bitmap-format image recorded without compression in an 8-bit or 16-bit format.
- This uncompressed format makes TIFF images suitable for saving images while maintaining the original high image quality.
- TIFF stands for Tagged Image File Format.
- HEIF image
- An irreversibly compressed image with higher compression than JPEG images.
- HEIF images can be converted and saved as JPEGs or TIFFs in DPP.
- HEIF stands for High Efficiency Image File format.
- Recipe
- The information on RAW image processing conditions that can be edited in DPP is called a recipe.
- As with RAW images, DPP also enables JPEG and TIFF image editing with recipes.
- bits
- Binary unit describing the volume information for image color, expressed as the number of bits per pixel.
- More bits enables more colors and smoother gradation. A one-bit image is black and white.
- Color management system (color matching)
- Digital cameras that capture images, monitors that display images, and printers that print images each have a different way of producing color. For this reason, there may be differences between the colors of an image as viewed on a monitor and as printed.
- Color management systems help make these colors more consistent. With DPP, ICC profiles can be used for a closer match between the colors of different devices.
- ICC profile
- ICC profiles are files containing color information such as color characteristics and color space for various devices, based on standards of the International Color Consortium, or ICC. Most devices, including monitors for viewing images or printers for printing images, can be color-managed using these ICC profiles, which can more closely match colors between devices.
- Color management in DPP applies ICC profiles.
- Tone curve
- A tone curve shows values before adjustment (input) on the horizontal axis of a graph and values after adjustment (output) on the vertical axis. Before adjustment, the values before and after adjustment are the same, which makes the tone curve a straight line from the lower left to the upper right, and by changing this tone curve, you can precisely adjust image brightness, contrast, and color. The further right on the horizontal axis or the higher on the vertical axis, the more positive the value becomes.
- Color space
-
A color space is the reproducible color range (color gamut characteristics). DPP supports the following color spaces.
sRGB:
Standard Windows color space. The standard color space of most monitors, digital cameras, and scanners.
Adobe RGB:
A wider color space than sRGB. Mainly used in applications such as commercial printing.
Apple RGB:
Standard Macintosh color space. Slightly wider than sRGB.
ColorMatch RGB:
A slightly wider color space than sRGB that is mainly used in applications such as commercial printing.
Wide Gamut RGB:
A wider color space than Adobe RGB.
The area covered by each color space is shown on the following chromaticity diagram.
Chromaticity diagram of DPP-compatible color spaces
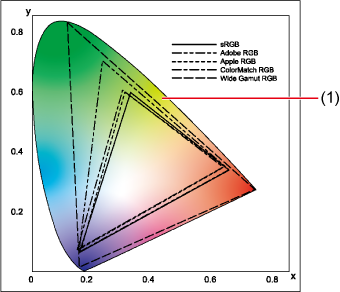
- Range of colors perceptible to the human eye
Gamma value White point (color temp.) 
RGB 2.2 6500 K (D65) 
Adobe RGB 2.2 6500 K (D65) 
Apple RGB 1.8 6500 K (D65) 
ColorMatch RGB 1.8 5000 K (D50) 
Wide Gamut RGB 2.2 5000 K (D50) - CMYK simulation profile
-
A profile that simulates the colors used in CMYK printing by printing presses and other equipment. DPP offers the following color simulation profiles.
-
Euro Standard:
Profile normally used for book printing in Europe, suitable for simulation of standard European printing.
-
JMPA:
Profile normally used for book printing and other purposes in Japan, suitable for simulation of printing under Japan Magazine Publishers Association guidelines.
-
U.S. Web Coated:
Profile normally used for book printing in North America, suitable for simulation of standard North American printing.
-
Japan Color 2001 Type 3:
Profile becoming a standard in the Japanese printing industry, suitable for simulation of standard Japan Color printing.
-
- Rendering intent
-
Rendering intents are color conversion methods used when images are printed.
-
Perceptual:
All colors are converted to maintain the relationship between colors before and after conversion. Even if colors are slightly different, this method enables printing natural-looking images with gradation maintained. Note that overall saturation for some images may change.
-
Relative colorimetric:
In-gamut colors are largely unchanged, and out-of-gamut colors are converted appropriately. Because most colors in images do not change much, this method enables printing natural-looking images without significant changes in saturation. Note that tones of some images may look slightly different, due to changes in highlights and out-of-gamut colors.
-